Transformers documentation
최적화
최적화
.optimization 모듈은 다음을 제공합니다:
- 미세 조정된 모델에 사용할 수 있는 가중치 감쇠가 적용된 옵티마이저
_LRSchedule을 상속받는 스케줄 객체 형태의 여러 스케줄- 여러 배치의 그래디언트를 누적하는 그래디언트 누적 클래스
AdaFactor (PyTorch)
class transformers.Adafactor
< source >( params lr = None eps = (1e-30, 0.001) clip_threshold = 1.0 decay_rate = -0.8 beta1 = None weight_decay = 0.0 scale_parameter = True relative_step = True warmup_init = False )
Parameters
- params (
Iterable[nn.parameter.Parameter]) — Iterable of parameters to optimize or dictionaries defining parameter groups. - lr (
float, optional) — The external learning rate. - eps (
tuple[float, float], optional, defaults to(1e-30, 0.001)) — Regularization constants for square gradient and parameter scale respectively - clip_threshold (
float, optional, defaults to 1.0) — Threshold of root mean square of final gradient update - decay_rate (
float, optional, defaults to -0.8) — Coefficient used to compute running averages of square - beta1 (
float, optional) — Coefficient used for computing running averages of gradient - weight_decay (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — Weight decay (L2 penalty) - scale_parameter (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — If True, learning rate is scaled by root mean square - relative_step (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — If True, time-dependent learning rate is computed instead of external learning rate - warmup_init (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Time-dependent learning rate computation depends on whether warm-up initialization is being used
AdaFactor pytorch implementation can be used as a drop in replacement for Adam original fairseq code: https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq/blob/master/fairseq/optim/adafactor.py
Paper: Adafactor: Adaptive Learning Rates with Sublinear Memory Cost https://huggingface.co/papers/1804.04235 Note that
this optimizer internally adjusts the learning rate depending on the scale_parameter, relative_step and
warmup_init options. To use a manual (external) learning rate schedule you should set scale_parameter=False and
relative_step=False.
This implementation handles low-precision (FP16, bfloat) values, but we have not thoroughly tested.
Recommended T5 finetuning settings (https://discuss.huggingface.co/t/t5-finetuning-tips/684/3):
Training without LR warmup or clip_threshold is not recommended.
- use scheduled LR warm-up to fixed LR
- use clip_threshold=1.0 (https://huggingface.co/papers/1804.04235)
Disable relative updates
Use scale_parameter=False
Additional optimizer operations like gradient clipping should not be used alongside Adafactor
Example:
Adafactor(model.parameters(), scale_parameter=False, relative_step=False, warmup_init=False, lr=1e-3)Others reported the following combination to work well:
Adafactor(model.parameters(), scale_parameter=True, relative_step=True, warmup_init=True, lr=None)When using lr=None with Trainer you will most likely need to use AdafactorSchedule
scheduler as following:
from transformers.optimization import Adafactor, AdafactorSchedule
optimizer = Adafactor(model.parameters(), scale_parameter=True, relative_step=True, warmup_init=True, lr=None)
lr_scheduler = AdafactorSchedule(optimizer)
trainer = Trainer(..., optimizers=(optimizer, lr_scheduler))Usage:
# replace AdamW with Adafactor
optimizer = Adafactor(
model.parameters(),
lr=1e-3,
eps=(1e-30, 1e-3),
clip_threshold=1.0,
decay_rate=-0.8,
beta1=None,
weight_decay=0.0,
relative_step=False,
scale_parameter=False,
warmup_init=False,
)step
< source >( closure = None )
Performs a single optimization step
스케줄
학습률 스케줄 (PyTorch)
class transformers.SchedulerType
< source >( value names = None module = None qualname = None type = None start = 1 )
Scheduler names for the parameter lr_scheduler_type in TrainingArguments.
By default, it uses “linear”. Internally, this retrieves get_linear_schedule_with_warmup scheduler from Trainer.
Scheduler types:
- “linear” = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup()
- “cosine” = get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup()
- “cosine_with_restarts” = get_cosine_with_hard_restarts_schedule_with_warmup()
- “polynomial” = get_polynomial_decay_schedule_with_warmup()
- “constant” = get_constant_schedule()
- “constant_with_warmup” = get_constant_schedule_with_warmup()
- “inverse_sqrt” = get_inverse_sqrt_schedule()
- “reduce_lr_on_plateau” =
get_reduce_on_plateau_schedule() - “cosine_with_min_lr” =
get_cosine_with_min_lr_schedule_with_warmup() - “cosine_warmup_with_min_lr” =
get_cosine_with_min_lr_schedule_with_warmup_lr_rate() - “warmup_stable_decay” = get_wsd_schedule()
transformers.get_scheduler
< source >( name: typing.Union[str, transformers.trainer_utils.SchedulerType] optimizer: Optimizer num_warmup_steps: typing.Optional[int] = None num_training_steps: typing.Optional[int] = None scheduler_specific_kwargs: typing.Optional[dict] = None )
Parameters
- name (
strorSchedulerType) — The name of the scheduler to use. - optimizer (
torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer that will be used during training. - num_warmup_steps (
int, optional) — The number of warmup steps to do. This is not required by all schedulers (hence the argument being optional), the function will raise an error if it’s unset and the scheduler type requires it. - num_training_steps (`int“, optional) — The number of training steps to do. This is not required by all schedulers (hence the argument being optional), the function will raise an error if it’s unset and the scheduler type requires it.
- scheduler_specific_kwargs (
dict, optional) — Extra parameters for schedulers such as cosine with restarts. Mismatched scheduler types and scheduler parameters will cause the scheduler function to raise a TypeError.
Unified API to get any scheduler from its name.
transformers.get_constant_schedule
< source >( optimizer: Optimizer last_epoch: int = -1 )
Create a schedule with a constant learning rate, using the learning rate set in optimizer.
transformers.get_constant_schedule_with_warmup
< source >( optimizer: Optimizer num_warmup_steps: int last_epoch: int = -1 )
Create a schedule with a constant learning rate preceded by a warmup period during which the learning rate increases linearly between 0 and the initial lr set in the optimizer.
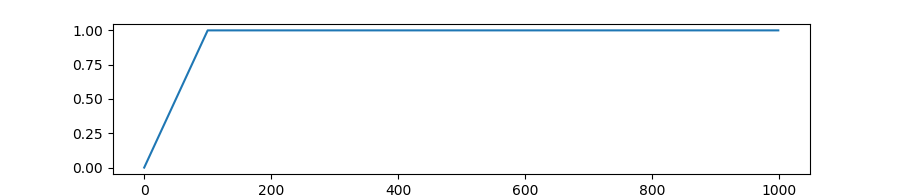
transformers.get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup
< source >( optimizer: Optimizer num_warmup_steps: int num_training_steps: int num_cycles: float = 0.5 last_epoch: int = -1 )
Parameters
- optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate. - num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup phase. - num_training_steps (
int) — The total number of training steps. - num_cycles (
float, optional, defaults to 0.5) — The number of waves in the cosine schedule (the defaults is to just decrease from the max value to 0 following a half-cosine). - last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with a learning rate that decreases following the values of the cosine function between the initial lr set in the optimizer to 0, after a warmup period during which it increases linearly between 0 and the initial lr set in the optimizer.
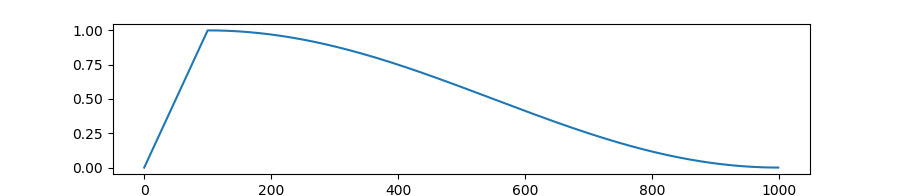
transformers.get_cosine_with_hard_restarts_schedule_with_warmup
< source >( optimizer: Optimizer num_warmup_steps: int num_training_steps: int num_cycles: int = 1 last_epoch: int = -1 )
Parameters
- optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate. - num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup phase. - num_training_steps (
int) — The total number of training steps. - num_cycles (
int, optional, defaults to 1) — The number of hard restarts to use. - last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with a learning rate that decreases following the values of the cosine function between the initial lr set in the optimizer to 0, with several hard restarts, after a warmup period during which it increases linearly between 0 and the initial lr set in the optimizer.
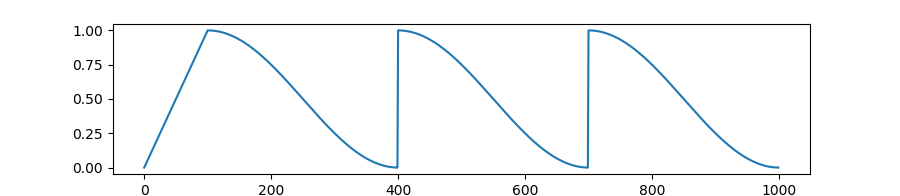
transformers.get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
< source >( optimizer num_warmup_steps num_training_steps last_epoch = -1 )
Parameters
- optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate. - num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup phase. - num_training_steps (
int) — The total number of training steps. - last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with a learning rate that decreases linearly from the initial lr set in the optimizer to 0, after a warmup period during which it increases linearly from 0 to the initial lr set in the optimizer.
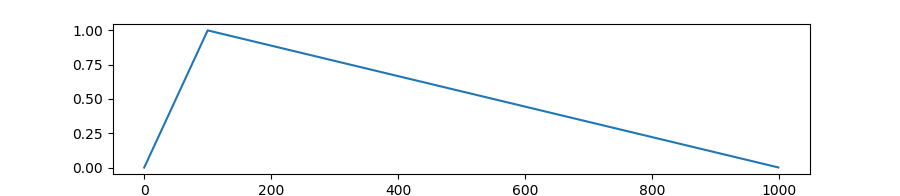
transformers.get_polynomial_decay_schedule_with_warmup
< source >( optimizer num_warmup_steps num_training_steps lr_end = 1e-07 power = 1.0 last_epoch = -1 )
Parameters
- optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate. - num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup phase. - num_training_steps (
int) — The total number of training steps. - lr_end (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-7) — The end LR. - power (
float, optional, defaults to 1.0) — Power factor. - last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with a learning rate that decreases as a polynomial decay from the initial lr set in the optimizer to end lr defined by lr_end, after a warmup period during which it increases linearly from 0 to the initial lr set in the optimizer.
Note: power defaults to 1.0 as in the fairseq implementation, which in turn is based on the original BERT implementation at https://github.com/google-research/bert/blob/f39e881b169b9d53bea03d2d341b31707a6c052b/optimization.py#L37
transformers.get_inverse_sqrt_schedule
< source >( optimizer: Optimizer num_warmup_steps: int timescale: typing.Optional[int] = None last_epoch: int = -1 )
Parameters
- optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate. - num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup phase. - timescale (
int, optional, defaults tonum_warmup_steps) — Time scale. - last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with an inverse square-root learning rate, from the initial lr set in the optimizer, after a warmup period which increases lr linearly from 0 to the initial lr set in the optimizer.
transformers.get_wsd_schedule
< source >( optimizer: Optimizer num_warmup_steps: int num_decay_steps: int num_training_steps: typing.Optional[int] = None num_stable_steps: typing.Optional[int] = None warmup_type: str = 'linear' decay_type: str = 'cosine' min_lr_ratio: float = 0 num_cycles: float = 0.5 last_epoch: int = -1 )
Parameters
- optimizer (
~torch.optim.Optimizer) — The optimizer for which to schedule the learning rate. - num_warmup_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the warmup phase. - num_decay_steps (
int) — The number of steps for the decay phase. - num_training_steps (
int, optional) — The total number of training steps. This is the sum of the warmup, stable and decay steps. Ifnum_stable_stepsis not provided, the stable phase will benum_training_steps - num_warmup_steps - num_decay_steps. - num_stable_steps (
int, optional) — The number of steps for the stable phase. Please ensure thatnum_warmup_steps + num_stable_steps + num_decay_stepsequalsnum_training_steps, otherwise the other steps will default to the minimum learning rate. - warmup_type (
str, optional, defaults to “linear”) — The type of warmup to use. Can be ‘linear’, ‘cosine’ or ‘1-sqrt’. - decay_type (
str, optional, defaults to “cosine”) — The type of decay to use. Can be ‘linear’, ‘cosine’ or ‘1-sqrt’. - min_lr_ratio (
float, optional, defaults to 0) — The minimum learning rate as a ratio of the initial learning rate. - num_cycles (
float, optional, defaults to 0.5) — The number of waves in the cosine schedule (the defaults is to just decrease from the max value to 0 following a half-cosine). - last_epoch (
int, optional, defaults to -1) — The index of the last epoch when resuming training.
Create a schedule with a learning rate that has three stages:
- warmup: increase from min_lr_ratio times the initial learning rate to the initial learning rate following a warmup_type.
- stable: constant learning rate.
- decay: decrease from the initial learning rate to min_lr_ratio times the initial learning rate following a decay_type.